一周几道算法题!
本周算法以动态规划为主,题解如下:
- Unique Paths || 🍉 🍉 🍉 dp
- Group the People Given the Group Size They Belong To 🍉 🍉 greedy
- Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree 🍉 tree
- Deepest Leaves Sum 🍉🍉 tree
- Max Increase to Keep City Skyline 🍉🍉
- Unique Paths || 🍉 🍉 🍉 dp
- Group the People Given the Group Size They Belong To 🍉 🍉 greedy
- Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree 🍉 tree
- Deepest Leaves Sum 🍉🍉 tree
- Max Increase to Keep City Skyline 🍉🍉
- Matrix Block Sum 🍉 🍉 🍉 dp
- Count Square Submatrices with All Ones 🍉 🍉🍉 dp
- House Robber 🍉 dp
- House Robber || 🍉🍉dp
Unique Paths ||
指数:🍉 🍉 🍉
思路:不算难,多模拟几次就能发现思路,边界条件永远要注意!
机器人从左上角走到右下角,每次要么向下要么向右。中间如果是1,就不能走。那么自然而然可以推出能够达到当前所在位置的只有从它上面或者左面走过来,即能到当前位置的路径数目是上面位置以及左面位置路径之和。于是得到状态方程:
dp[i][j] = d[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]当然这里一些边界条件的细节需要注意一下。
算法时间空间复杂度都是$O(mn)$
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>>& obs) {
int n = obs.size();
int m = obs[0].size();
if (obs[n-1][m-1] == 1 || obs[0][0] == 1) return 0;
vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int> (m, 0));
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++){
if(dp[i-1][0] && !obs[i][0])
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int i=1; i<m; i++){
if(dp[0][i-1] && !obs[0][i])
dp[0][i] = 1;
}
for (int i=1; i<n; i++)
for (int j=1; j<m; j++){
if (!obs[i][j])
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}
return dp[n-1][m-1];
}
};
同样思路的python代码很简单。
Python3:
class Solution:
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, A: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n, m = len(A), len(A[0])
if A[n-1][m-1] == 1 or A[0][0] == 1:
return 0
dp = [[0]*m for _ in range(n)]
dp[0][0] = 1
for i in range(1, n):
if dp[i-1][0] and A[i][0]!=1:
dp[i][0] = 1
for j in range(1, m):
if dp[0][j-1] and A[0][j]!=1:
dp[0][j] = 1
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(1, m):
if A[i-1][j] != 1:
dp[i][j] += dp[i-1][j]
if A[i][j-1] != 1:
dp[i][j] += dp[i][j-1]
return dp[-1][-1]Group the People Given the Group Size They Belong To
指数:🍉🍉
思路: 每个人属于不同大小的组,只要组的大小对,组里其他人是谁都不用管。直观上,只需要把人按组的大小归类得到若干大组,然后再按大组进行小组划分即可。
python:
class Solution(object):
def groupThePeople(self, A):
"""
:type groupSizes: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
n = len(A)
mat = [[] * (n+1) for _ in range(n+1)]
for i, c in enumerate(A):
mat[c].append(i)
res = []
for i in range(n+1):
cl = len(mat[i])
if cl > 0:
j = 0
while j < cl:
res.append(mat[i][j:j+i])
j = j + i
return resc++:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> groupThePeople(vector<int>& A) {
int n = A.size();
unordered_map<int,vector<int>> mp;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
mp[A[i]].push_back(i);
vector<vector<int>> v;
for(auto m:mp) {
int n = m.second.size(), i = 0;
while (i<n) {
vector<int> res;
int k = m.first;
while (k--&&i<n)
res.push_back(m.second[i++]);
v.push_back(res);
}
}
return v;
}
};
Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
指数:🍉
思路:有一棵树及其克隆树,给定原始树上某个节点,找克隆树上对应的节点。层次遍历。树的层次遍历使用队列。
python:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def getTargetCopy(self, original: TreeNode, cloned: TreeNode, target: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
oq = [original]
cq = [cloned]
while oq:
ocur = oq.pop(0)
ccur = cq.pop(0)
if ocur == target:
return ccur
if ocur.left:
oq.append(ocur.left)
cq.append(ccur.left)
if ocur.right:
oq.append(ocur.right)
cq.append(ccur.right)Deepest Leaves Sum
指数:🍉🍉
思路:给定一棵树,返回最深的叶节点之和。最深的叶节点就在最后一层,所以直观上通过层次遍历就可以取到最后一层所有的节点了,之后再进行求和。
python:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def deepestLeavesSum(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
q = []
if root:
q.append(root)
levels = []
while q:
level = []
lenq = len(q)
for i in range(lenq):
cur = q.pop(0)
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
level.append(cur.val)
levels.append(level)
return sum(levels[-1])Max Increase to Keep City Skyline
指数:🍉🍉
思路: 首先要理解City Skyline这个概念,即都市天际线。其特点是从上面和从下面看是相同的,左右是相同的。那么为了保持天际线,增加高度时需要保持不超过上下和左右的最高建筑。即小于等于二者较小值。理清这个思路,找准对应的位置即可写出代码。
python:
class Solution:
def maxIncreaseKeepingSkyline(self, A: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n, m = len(A), len(A[0])
# Get top/bottom skyline
T = [max([A[j][i] for j in range(n)]) for i in range(m)]
# Get left/right skyline
L = [max(A[i][:]) for i in range(n)]
cnt = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
cnt += min(T[j], L[i]) - A[i][j]
return cntMatrix Block Sum
指数:🍉🍉🍉
思路: 这可以算是一道数学问题,核心是计算二维数组的前缀和,通过前缀和简化answer矩阵元素的计算。
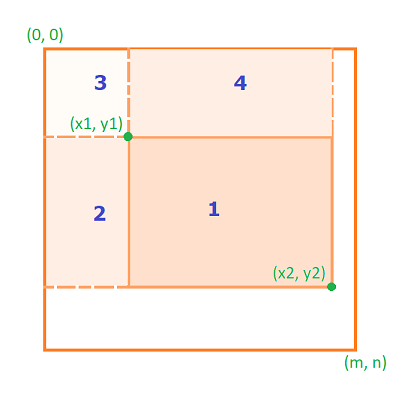
首先本题借用leetcode上的一张图来解释。$area1 = area{1+2+3+4} - area{2+3} - area{3+4} + area_3$
二维数组前缀和求法:
以当前位置为右下角的matrix的二维数组的和,即:
$$prefix(x2, y2) = matrix(x2, y2) + prefix(x1,y2) + prefix(x2, y1) - prefix(x1, y1)$$
python:
class Solution:
def matrixBlockSum(self, mat: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
# 一道数学问题,核心是计算二维数组的前缀和,通过前缀和简化answer矩阵元素的计算
# 二维数组前缀和
n, m = len(mat), len(mat[0])
psum = [[0] * (m+1) for _ in range(n+1)]
for i in range(1, n+1):
for j in range(1, m+1):
# 左边+上边-交叉部分
psum[i][j] = mat[i-1][j-1] + psum[i-1][j] + psum[i][j-1] - psum[i-1][j-1]
ans = [[0] * m for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
x1, y1 = min(n-1, i+k)+1, min(m-1, j+k)+1
x2, y2 = max(-1, i-k-1)+1, max(-1, j-k-1)+1
ans[i][j] = psum[x1][y1] - psum[x2][y1] - psum[x1][y2] + psum[x2][y2]
return ansCount Square Submatrices with All Ones
指数:🍉🍉🍉
思路: 给定 $m*n$ 的一个01矩阵,返回全1的方形矩阵的数量。单个1也算(边长为1的正方形)。
首先,判断出用动态规划解。(子问题、无后效性、最优子结构)
接下来重点在于理解当前位置$(i,j)$所能构成的最大边长的正方形取决于什么。看一个例子:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 n 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 j 0 0
0 0 0 0 m i 0 0 0 当前位置$(i,j)$所能构成的最大边长的正方形受三方面的限制,上、左、左上。三者但凡有一个短板就会影响当前位置所能构成正方形的最大边长。
python:
class Solution:
def countSquares(self, A: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n, m = len(A), len(A[0])
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(1, m):
if A[i][j]:
A[i][j] += min(A[i-1][j-1], A[i-1][j], A[i][j-1])
return sum(map(sum, A))House Robber
指数:🍉
思路: 经典的dp问题,需要弄明白当前位置取不取的判断标准。取就说明,取了i,那么加上之前最大的i-2,比i-1位置的和要大。即:
$ans[i+1] = max(ans[i], ans[i-1] + nums[i])$.
python:
class Solution:
def rob(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(nums)
if n <= 1: return sum(nums)
me = [0] * (n+1)
me[1] = nums[0]
for i in range(n):
me[i+1] = max(me[i], me[i-1] + nums[i])
return me[-1]House Robber II
指数:🍉🍉
思路:和上一题的区别在于现在数据以环状连接,即第一个和最后一个不能同时取。问题转换为在[0,n-2]和[1,n-1]两个区间里分别求最大,最后取二者大的那个即可。
